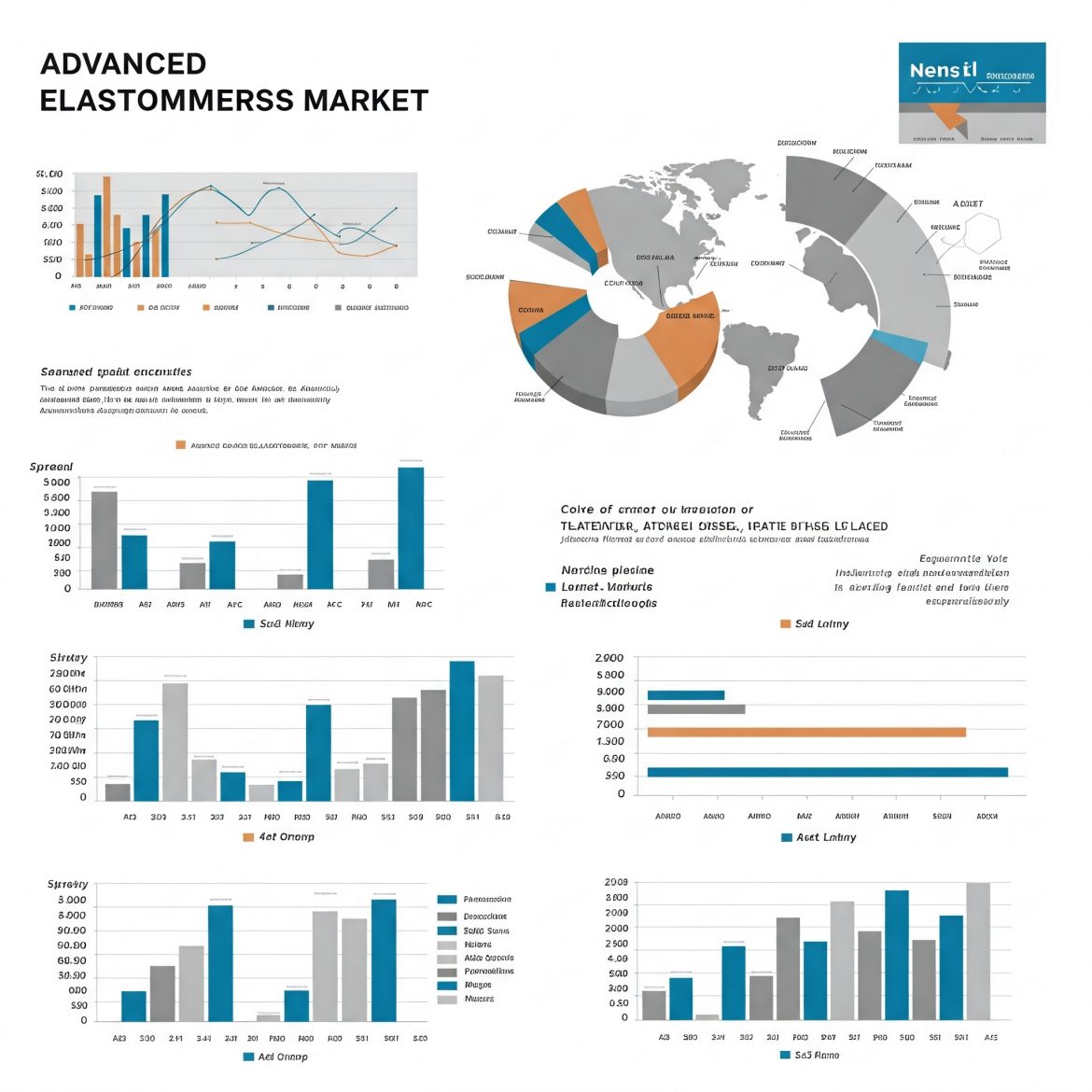
Advanced Elastomers: Properties, Applications, and Future Trends
Introduction
Elastomers are rubber-like polymeric materials that can be stretched and revert to their original form without undergoing permanent deformation. Advanced elastomers are a new generation of these materials that possess superior mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties designed for high-performance applications. Advanced elastomers are an essential part of industries like automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and electronics because of their high durability and versatility.
Properties of Advanced Elastomers
High-performance elastomers are designed to possess superior properties that make them capable of handling rigorous applications. Their most important characteristics are:
High Elasticity and Resilience – They are able to extend several times their original size and regain their form without any deformation.
Improved Thermal Stability – In contrast to normal rubber, high-performance elastomers are capable of withstanding severe temperatures, thus being suitable for high-temperature conditions.
Chemical and Solvent Resistance – Most modern elastomers resist oils, fuels, and severe chemicals, which guarantee durability in harsh environments.
Mechanical Strength – Reinforced elastomers provide enhanced tensile strength, tear resistance, and abrasion resistance.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity – Some elastomers are designed to carry electricity or disperse heat, making them worthwhile in electronic and thermal management applications.
Types of Advanced Elastomers
There are a variety of advanced elastomers, all with particular applications:
Silicone Elastomers – With excellent heat stability, flexibility, and biocompatibility, they have extensive use in medical devices, electronics, and aerospace.
Fluoroelastomers (FKM) – With superb chemical, oil, and high-temperature resistance, they are critical for the automotive and aerospace industries.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs) – Blending the properties of rubber and plastic, TPEs provide recyclability, processability, and versatility in end uses like consumer products, medical devices, and automotive parts.
Polyurethane Elastomers – Known for their abrasion resistance and toughness, they find application in industrial coatings, seals, and mechanical components.
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) – An advanced elastomer that finds application in medical implants, electrical insulators, and precision molded parts because of its purity and longevity.
Uses of Advanced Elastomers
The specific properties of advanced elastomers make them a vital requirement in several industries:
Automotive Industry – Finds application in seals, gaskets, hoses, vibration dampeners, and fuel system components because of their resistance to fuels, oils, and high temperatures.
Aerospace Industry – Fluoroelastomers and silicone elastomers find significant application in sealing and insulation applications where chemical and high temperature resistance is needed.
Healthcare and Medical Devices – Silicone and LSR are utilized for prosthetics, catheters, tubing, and implants because of their biocompatibility and sterilization.
Electronics and Electrical Engineering – Thermally conductive elastomers facilitate heat dissipation in electronic devices, while flexible elastomers are employed in wearable electronics and flexible circuits.
Industrial and Manufacturing – Elastomers are employed in conveyor belts, rollers, seals, and protective coatings for machinery and equipment.
Future Trends and Innovations
Development and research in elastomer technology continue to push innovations, with emphasis on sustainability, performance improvement, and multifunctionality.
The major trends are:
Sustainable Elastomers – With the drive for sustainable materials, there have been the creation of bio-based and recyclable elastomers to lower environmental footprint.
Smart Elastomers – Self-healing, shape memory, or stimulus response materials are being developed for robotics, biomedical, and adaptive materials applications.
Nanocomposite Elastomers – Adding nanomaterial like graphene or carbon nanotube increases mechanical toughness, conductivity, and barrier performance.
3D-Printed Elastomers – Additive manufacturing is facilitating the development of elastomeric components with intricate geometries and customized properties for medical and industrial uses.
Conclusion
Elastomers of advanced nature are transforming industries across the board through superior mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties engineered for high-performance applications. As technology continues to evolve, further development of sustainable, smart, and high-performance elastomers will continue to expand their potential and fuel innovations across various sectors.
GET MORE DATA
chris@marketinsightsresearch.com